The following consolidated Query from all the DMV's should give the missing indexes in the table
SELECT
statement AS [database.scheme.table],
column_id , column_name, column_usage,
migs.user_seeks, migs.user_scans,
migs.last_user_seek, migs.avg_total_user_cost,
migs.avg_user_impact
FROM sys.dm_db_missing_index_details AS mid
CROSS APPLY sys.dm_db_missing_index_columns (mid.index_handle)
INNER JOIN sys.dm_db_missing_index_groups AS mig
ON mig.index_handle = mid.index_handle
INNER JOIN sys.dm_db_missing_index_group_stats AS migs
ON mig.index_group_handle=migs.group_handle
ORDER BY mig.index_group_handle, mig.index_handle, column_id
GO
When you create indexes , Please note the following
a. The DML operations will become slow if there are many indexes
b. More diskspace is required if you create more indexes..Also depends on the column datatype.
c. Create 100% fill factor on the indexes if the table is used only for read purposes; For all other DML operations balance the fillfactor between 0 and 100 percent.
Monday, January 19, 2009
Monday, August 11, 2008
Excel:Sorting Excel Sheets using VB Macro
Sub SortSheets()
Dim i As Integer, j As IntegerFor i = 1 To Sheets.Count
For j = 1 To Sheets.Count - 1
If UCase$(Sheets(j).Name) > UCase$(Sheets(j + 1).Name) Then
Sheets(j).Move after:=Sheets(j + 1)
End If
Next j
Next i
End Sub
Cleaning Phone Numbers using CTE
Cleaning Phone Numbers using the Common Table Expressions
Declare
@Str1 VarChar(max),
@Str2 VarChar(max);
Select
@Str1='(208)*/ 555-1212',
@Str2='';
With PhoneClean as
(
Select
Case
when SubString(@Str1,1,1) like '[0-9]' then SubString(@Str1,1,1)
else ''
End[Chr],
1[Idx]
Union All
Select
Case
when SubString(@Str1,Idx+1,1) like '[0-9]' then SubString(@Str1,Idx+1,1)
else ''
End,
Idx+1
from PhoneClean
where (Idx+1)<=Len(@Str1) ) Select @Str2=@Str2+Chr from PhoneClean option (MaxRecursion 0); Select @Str2;
Source:www.sqlservercentral.com
Friday, August 01, 2008
Getting the ForeignKeys Base and Reference Tables in a Database
select d.name as fk,b.name as base,c.name as ref from sysforeignkeys a, sysobjects b, sysobjects c,sysobjects d
where b.id=a.fkeyid
and c.id=a.rkeyid
and d.id=a.constid
where b.id=a.fkeyid
and c.id=a.rkeyid
and d.id=a.constid
Sending Email in SSIS without using the Sendmail Task
Using the System.Web.Mail To send an attachment along with the email
Imports System.Web.Mail
Public Sub Main()
Dim message As MailMessage = New System.Web.Mail.MailMessage()
Dim Att As String
Att = Dts.Variables("Attachments").Value.ToString
Att = Att & Now.Day.ToString & Now.Month.ToString & Now.Year.ToString & ".xls"
'MsgBox(Att.ToString)
message.From = ""
message.To = ""
message.Subject = "Abandoned Emails " & Now.Day.ToString & Now.Month.ToString & Now.Year.ToString
Dim oattach As MailAttachment = New MailAttachment(Att)
message.Attachments.Add(oattach)
SmtpMail.SmtpServer = ""
SmtpMail.Send(message)
Dts.TaskResult = Dts.Results.Success
End Sub
End Class
Imports System.Web.Mail
Public Sub Main()
Dim message As MailMessage = New System.Web.Mail.MailMessage()
Dim Att As String
Att = Dts.Variables("Attachments").Value.ToString
Att = Att & Now.Day.ToString & Now.Month.ToString & Now.Year.ToString & ".xls"
'MsgBox(Att.ToString)
message.From = "
message.To = "
message.Subject = "Abandoned Emails " & Now.Day.ToString & Now.Month.ToString & Now.Year.ToString
Dim oattach As MailAttachment = New MailAttachment(Att)
message.Attachments.Add(oattach)
SmtpMail.SmtpServer = "
SmtpMail.Send(message)
Dts.TaskResult = Dts.Results.Success
End Sub
End Class
Friday, July 11, 2008
Who receives the email when a job fails?
Here is a script that gives you the list of operators name who receive notifications when a job fails
SELECT sysoperators.name AS JobName, sysjobs.name AS OperatorName, sysjobs.enabled, sysoperators.id
FROM sysjobs INNER JOIN
sysoperators ON sysjobs.notify_email_operator_id = sysoperators.id
You need to change the sysjobs.notify_email_operator_id to change the Notifications of the Operator.
SELECT sysoperators.name AS JobName, sysjobs.name AS OperatorName, sysjobs.enabled, sysoperators.id
FROM sysjobs INNER JOIN
sysoperators ON sysjobs.notify_email_operator_id = sysoperators.id
You need to change the sysjobs.notify_email_operator_id to change the Notifications of the Operator.
Tuesday, July 08, 2008
When the Procedures were last modified
SELECT name, create_date, datepart(dy,create_date) as CreatedDayOfYear,
modify_date, datepart(dy,modify_date) as ModificationDayOfYear
FROM sys.sql_modules
JOIN sys.objects
ON sys.sql_modules.object_id = sys.objects.object_id
AND TYPE = 'P'
order by datepart(yyyy,modify_date) desc,
datepart(dy,modify_date) desc, name;
modify_date, datepart(dy,modify_date) as ModificationDayOfYear
FROM sys.sql_modules
JOIN sys.objects
ON sys.sql_modules.object_id = sys.objects.object_id
AND TYPE = 'P'
order by datepart(yyyy,modify_date) desc,
datepart(dy,modify_date) desc, name;
Monday, July 07, 2008
SSMS tools Pack
I found this new tool pack on Google Search...
http://www.ssmstoolspack.com/
Quite Useful for automating certain things on SQL SERVER
and this is how to create addins on SQL SERVER
http://aspalliance.com/1374_Extend_Functionality_in_SQL_Server_2005_Management_Studio_with_Addins.all
http://www.ssmstoolspack.com/
Quite Useful for automating certain things on SQL SERVER
and this is how to create addins on SQL SERVER
http://aspalliance.com/1374_Extend_Functionality_in_SQL_Server_2005_Management_Studio_with_Addins.all
Friday, June 27, 2008
Executing the Same Query across all Databases
Eg:
Declare @sql varchar(1000)
set @Sql = 'select * from Contacts'
select 'use ' + name +
' ' + @sql from master.dbo.sysdatabases where dbid > 4
Copy the Statements to a new window and execute it.
Declare @sql varchar(1000)
set @Sql = 'select * from Contacts'
select 'use ' + name +
' ' + @sql from master.dbo.sysdatabases where dbid > 4
Copy the Statements to a new window and execute it.
Wednesday, June 25, 2008
Backup Report for the Server
Reports the ServerName , Database Name and LastBackupDate
select Convert(Varchar(25),server_name) as 'Server Name'
,convert(varchar(25),database_name) as 'Database'
,getdate() as reportdate, max(backup_finish_date) as 'Last_backup_date'
from msdb..backupset
Where database_name
in
(select name from master..sysdatabases)
and server_name = @@servername
group by server_name,database_name order by Last_backup_date DESC
select Convert(Varchar(25),server_name) as 'Server Name'
,convert(varchar(25),database_name) as 'Database'
,getdate() as reportdate, max(backup_finish_date) as 'Last_backup_date'
from msdb..backupset
Where database_name
in
(select name from master..sysdatabases)
and server_name = @@servername
group by server_name,database_name order by Last_backup_date DESC
Script for Changing the Job Owners across all the Jobs
Change the Owner of all the SQL Agent Jobs using the Following Script
SELECT 'EXEC MSDB.dbo.sp_update_job ' + char(13) +
'@job_name = ' + char(39) + j.[Name] + char(39) + ',' + char(13) +
'@owner_login_name = ' + char(39) + 'sa' + char(39) + char(13) + char(13)
FROM MSDB.dbo.sysjobs j
INNER JOIN Master.dbo.syslogins l
ON j.owner_sid = l.sid
WHERE l.[name] <> 'sa'
ORDER BY j.[name]
SELECT 'EXEC MSDB.dbo.sp_update_job ' + char(13) +
'@job_name = ' + char(39) + j.[Name] + char(39) + ',' + char(13) +
'@owner_login_name = ' + char(39) + 'sa' + char(39) + char(13) + char(13)
FROM MSDB.dbo.sysjobs j
INNER JOIN Master.dbo.syslogins l
ON j.owner_sid = l.sid
WHERE l.[name] <> 'sa'
ORDER BY j.[name]
Thursday, April 24, 2008
Using sp_send_dbmail in HTML format
Using sp_send_dbmail , the data in sql server can be sent in HTML format.
Eg:
I have a HTML file in the follwing format
and is saved as web.htm in a network location.
Here is the TSQL script that will send an email to a recipient in the HTML format using web.htm
---------------
declare @cmdshell varchar(1000)
if exists(select * from #cmdtable)
drop table #cmdtable
create table #CMDTABLE(line varchar(2000))
insert into #cmdtable
exec xp_cmdshell 'type "\\Your Network Share\web.htm" '
select @cmdshell = line from #CMDTABLE
exec msdb.dbo.sp_send_dbmail
@recipients = 'your email address'
,@body = @cmdshell
,@body_format = 'HTML'
,@subject = 'Testing with web.txt'
can use the same stuff for attaching a picture on the HTML page
Eg:
I have a HTML file in the follwing format
and is saved as web.htm in a network location.
Here is the TSQL script that will send an email to a recipient in the HTML format using web.htm
---------------
declare @cmdshell varchar(1000)
if exists(select * from #cmdtable)
drop table #cmdtable
create table #CMDTABLE(line varchar(2000))
insert into #cmdtable
exec xp_cmdshell 'type "\\Your Network Share\web.htm" '
select @cmdshell = line from #CMDTABLE
exec msdb.dbo.sp_send_dbmail
@recipients = 'your email address'
,@body = @cmdshell
,@body_format = 'HTML'
,@subject = 'Testing with web.txt'
can use the same stuff for attaching a picture on the HTML page
Friday, May 11, 2007
Exporting Sql Server Table to MS Excel
Here is the Coding for Exporting the any Sql Server to Excel Sheet using VBA
a. Take an excel sheet and place the Database Name and Table name in any 2 cells as below
In my Sheet i placed the Database Name and Table name on cells M12 and cells M14 respectively.
Place a button just below them and enter the following code by creating a new Module in Visual Basic Editor(alt + F11)
Sub DataExtract()
Dim tablename As String
Dim Databasename As String
' Create a connection object.
Dim cnPubs As New ADODB.Connection
tablename = Range("M14").Value
Databasename = Range("M12").Value
Worksheets("Sheet2").Cells.ClearContents
Sheet2.Cells.Font.Name = "Tahoma"
Sheet2.Cells.Font.Size = "8"
'Provide the connection string.
Dim strConn As String
cnPubs.Provider = "sqloledb"
'Use the SQL Server OLE DB Provider.
strConn = "DATA SOURCE=Server Name;INITIAL CATALOG =" & Databasename & ";user id =;password = "
''Change the Connecting String (www.connectionstrings.com)
'Now open the connection.
cnPubs.Open strConn
Dim rsPubs As ADODB.Recordset
Set rsPubs = New ADODB.Recordset
With rsPubs
' Assign the Connection object.
.ActiveConnection = cnPubs
' Extract the required records.
.Open "SELECT * FROM " & tablename
' Copy the records into cell A1 on Sheet1.
Sheet2.Range("A1").CopyFromRecordset rsPubs
' Tidy up
.Close
End With
Sheet2.Rows.Font.Bold = False
Sheet2.Activate
Rows("1:1").Select
Selection.Insert Shift:=xlDown
Dim i As Integer
For i = 0 To rsPubs.Fields.Count - 1
Sheet2.Cells(1, i + 1) = rsPubs.Fields(i).Name
Next
Sheet2.Rows(1).Font.Bold = True
cnPubs.Close
Set rsPubs = Nothing
Set cnPubs = Nothing
End Sub
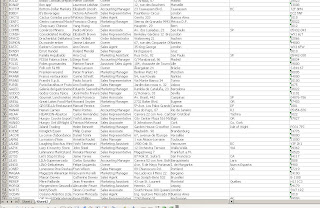
When the import button is clicked The Sql Server Table will be imported to Sheet 2 as below!!!
a. Take an excel sheet and place the Database Name and Table name in any 2 cells as below

In my Sheet i placed the Database Name and Table name on cells M12 and cells M14 respectively.
Place a button just below them and enter the following code by creating a new Module in Visual Basic Editor(alt + F11)
Sub DataExtract()
Dim tablename As String
Dim Databasename As String
' Create a connection object.
Dim cnPubs As New ADODB.Connection
tablename = Range("M14").Value
Databasename = Range("M12").Value
Worksheets("Sheet2").Cells.ClearContents
Sheet2.Cells.Font.Name = "Tahoma"
Sheet2.Cells.Font.Size = "8"
'Provide the connection string.
Dim strConn As String
cnPubs.Provider = "sqloledb"
'Use the SQL Server OLE DB Provider.
strConn = "DATA SOURCE=Server Name;INITIAL CATALOG =" & Databasename & ";user id =
''Change the Connecting String (www.connectionstrings.com)
'Now open the connection.
cnPubs.Open strConn
Dim rsPubs As ADODB.Recordset
Set rsPubs = New ADODB.Recordset
With rsPubs
' Assign the Connection object.
.ActiveConnection = cnPubs
' Extract the required records.
.Open "SELECT * FROM " & tablename
' Copy the records into cell A1 on Sheet1.
Sheet2.Range("A1").CopyFromRecordset rsPubs
' Tidy up
.Close
End With
Sheet2.Rows.Font.Bold = False
Sheet2.Activate
Rows("1:1").Select
Selection.Insert Shift:=xlDown
Dim i As Integer
For i = 0 To rsPubs.Fields.Count - 1
Sheet2.Cells(1, i + 1) = rsPubs.Fields(i).Name
Next
Sheet2.Rows(1).Font.Bold = True
cnPubs.Close
Set rsPubs = Nothing
Set cnPubs = Nothing
End Sub
When the import button is clicked The Sql Server Table will be imported to Sheet 2 as below!!!

Tuesday, May 01, 2007
Columns in CSV Format
Eg: The Popular Northwind Database.
Combine the Products and Orderdetails table with the Productid to get the Productname and name a new table as Product_orders
The Join is as follows
select
od.*,p.productname
from
[order details] od
join
products p
on
od.productid=p.productid
order by od.orderid
The Data is as follows

Now If you need all the products and the Quantity in per orderid in a single column like

so the Table looks like
OrderID Productname
343434 Product1,Quantity||Product2,Quantity||Product3,Quantity
Here is the Code Sample to do the Reporting Structure
--Create the table for orderid and allproducts as
create table result
(
orderid int
,Values_CSV varchar(8000)
)
--Use the Following Cursor Code
declare csno cursor for
select distinct orderid from product_orders
declare @snos int
open csno
fetch next from csno into @snos
declare @allvalues varchar(8000)
while @@fetch_status = 0
begin
set @allvalues=null
select @allvalues =isnull(@allvalues+'||','') + [productname]+','+convert(varchar(50),[quantity])
from product_orders
where orderid = @snos
insert into result values(@snos,@allvalues)
fetch next from csno into @snos
end
close csno
deallocate csno
Combine the Products and Orderdetails table with the Productid to get the Productname and name a new table as Product_orders
The Join is as follows
select
od.*,p.productname
from
[order details] od
join
products p
on
od.productid=p.productid
order by od.orderid
The Data is as follows

Now If you need all the products and the Quantity in per orderid in a single column like

so the Table looks like
OrderID Productname
343434 Product1,Quantity||Product2,Quantity||Product3,Quantity
Here is the Code Sample to do the Reporting Structure
--Create the table for orderid and allproducts as
create table result
(
orderid int
,Values_CSV varchar(8000)
)
--Use the Following Cursor Code
declare csno cursor for
select distinct orderid from product_orders
declare @snos int
open csno
fetch next from csno into @snos
declare @allvalues varchar(8000)
while @@fetch_status = 0
begin
set @allvalues=null
select @allvalues =isnull(@allvalues+'||','') + [productname]+','+convert(varchar(50),[quantity])
from product_orders
where orderid = @snos
insert into result values(@snos,@allvalues)
fetch next from csno into @snos
end
close csno
deallocate csno
Proper Case using Sql
Here is the Sql function that will Proper Case any column in a table
set ANSI_NULLS ON
set QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
GO
create function [dbo].[ProperCase](@Text as varchar(8000))
returns varchar(8000)
as
begin
declare @Reset bit;
declare @Ret varchar(8000);
declare @i int;
declare @c char(1);
select @Reset = 1, @i=1, @Ret = ''
while (@i <= len(@Text))
select @c= substring(@Text,@i,1),
@Ret = @Ret + case when @Reset=1 then UPPER(@c) else LOWER(@c) end,
@Reset = case when @c like '[a-zA-Z]' or @c in ('''') then 0 else 1 end,
@i = @i +1
return @Ret
end
--Example
declare @name varchar(100)
set @name ='brue willis'
set @name = dbo.propercase(@name)
print @name
Result -- Bruce Willis
set ANSI_NULLS ON
set QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
GO
create function [dbo].[ProperCase](@Text as varchar(8000))
returns varchar(8000)
as
begin
declare @Reset bit;
declare @Ret varchar(8000);
declare @i int;
declare @c char(1);
select @Reset = 1, @i=1, @Ret = ''
while (@i <= len(@Text))
select @c= substring(@Text,@i,1),
@Ret = @Ret + case when @Reset=1 then UPPER(@c) else LOWER(@c) end,
@Reset = case when @c like '[a-zA-Z]' or @c in ('''') then 0 else 1 end,
@i = @i +1
return @Ret
end
--Example
declare @name varchar(100)
set @name ='brue willis'
set @name = dbo.propercase(@name)
print @name
Result -- Bruce Willis
Monday, March 26, 2007
Stored Procedure for Searching any Value in a Table
This Stored Procedure is for Searching any value in any column in a table
Exec searchforvalues 'param1','param2'
param1 - Tablename
param2 - A String(including wildcard characters)
Use it for your Convienience!!!
---Coding---
alter procedure searchforvalues
@tablename nvarchar(100),@searchstring nvarchar(100)
as
declare @c_id nvarchar(1000)
declare @sstring nvarchar(1000)
declare @sql nvarchar(1000)
declare @String nvarchar(1000)
set nocount on
set @searchstring = ''''+@searchstring+''''
if exists(select * from information_schema.tables where table_name like +@tablename)
begin
if exists(select * from information_schema.tables where table_name like 'Sql_search')
begin
set @sql=''
set @sql=@sql+N'drop table Sql_search'
exec sp_executesql @sql
end
set @sql=''
set @sql=@sql+'create table Sql_search(column_name nvarchar(1000),searchstring nvarchar(1000))'
exec sp_executesql @sql
declare c1 cursor for
select column_name from information_schema.columns
where
table_name like @tablename
--Cursor Starts
open c1
fetch next from c1
into @c_id
while @@fetch_status = 0
begin
set @String =''''+@c_id+''''
set @sql=''
set @sql=@sql+'insert into sql_search select '+@string+',['+@c_id+'] from '+@tablename+' where ['+@c_id +'] like '+@searchstring
exec sp_executesql @sql
fetch next from c1
into @c_id
end
close c1
deallocate c1
--Cursor Ends
--Output
set @sql=''
set @sql=@sql+'select column_name,searchstring ,count(*) as [Count] from sql_search
group by column_name,searchstring
order by column_name'
exec sp_executesql @sql
print @sql
exec('drop table sql_search')
end
else
Print 'Table Does Not Exist'
Exec searchforvalues 'param1','param2'
param1 - Tablename
param2 - A String(including wildcard characters)
Use it for your Convienience!!!
---Coding---
alter procedure searchforvalues
@tablename nvarchar(100),@searchstring nvarchar(100)
as
declare @c_id nvarchar(1000)
declare @sstring nvarchar(1000)
declare @sql nvarchar(1000)
declare @String nvarchar(1000)
set nocount on
set @searchstring = ''''+@searchstring+''''
if exists(select * from information_schema.tables where table_name like +@tablename)
begin
if exists(select * from information_schema.tables where table_name like 'Sql_search')
begin
set @sql=''
set @sql=@sql+N'drop table Sql_search'
exec sp_executesql @sql
end
set @sql=''
set @sql=@sql+'create table Sql_search(column_name nvarchar(1000),searchstring nvarchar(1000))'
exec sp_executesql @sql
declare c1 cursor for
select column_name from information_schema.columns
where
table_name like @tablename
--Cursor Starts
open c1
fetch next from c1
into @c_id
while @@fetch_status = 0
begin
set @String =''''+@c_id+''''
set @sql=''
set @sql=@sql+'insert into sql_search select '+@string+',['+@c_id+'] from '+@tablename+' where ['+@c_id +'] like '+@searchstring
exec sp_executesql @sql
fetch next from c1
into @c_id
end
close c1
deallocate c1
--Cursor Ends
--Output
set @sql=''
set @sql=@sql+'select column_name,searchstring ,count(*) as [Count] from sql_search
group by column_name,searchstring
order by column_name'
exec sp_executesql @sql
print @sql
exec('drop table sql_search')
end
else
Print 'Table Does Not Exist'
Sunday, February 25, 2007
Stored Procedures - Removing Duplicates
The Following is a Simple Stored Procedure that flags a records as duplicate in a table where duplicate exists
a.Checks for the valid column and tablename.
b. Creates an Srn (identity column).
c. Creates a column dupe
d.Flags Dupes wherever duplicate records found
The Code for the Stored Procedure is as follows
GO
/****** Object: StoredProcedure [dbo].[remove_duplicates] ******/
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
GO
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
GO
ALTER procedure [dbo].[remove_duplicates]
@colname varchar(200)
,@tablename varchar(100)
as
set nocount on
declare @sql varchar(1000)
declare @no_duplicates int
--Check for the Table and Column Name
set @sql=''
if exists
(
select * from syscolumns where name like +''+@colname+'' and id = object_id(+''+@tablename+'')
)
begin
--Generate an SRN Number
if exists(select * from syscolumns where id = object_id(+''+@tablename+'') and name like 'Vic_srn')
begin
set @sql=''
set @sql = @sql + 'alter table '+@tablename+ ' drop column Vic_srn'
exec(@sql)
end
set @sql=''
set @sql = @sql+'alter table '+@tablename+ ' add Vic_srn numeric(6) identity(1,1)'
exec(@sql)
--Add a column for Dupes
if exists(select * from syscolumns where id = object_id(+''+@tablename+'') and name like 'dupes')
begin
set @sql=''
set @sql = @sql + 'alter table '+@tablename+ ' drop column dupes'
exec(@sql)
end
set @sql=''
set @sql=@sql+' alter table '+@tablename+ ' add dupes varchar(10)'
exec(@sql)
--Update the Column Dupes
set @sql=''
set @sql=@sql+'update a '+char(13)
+'set a.dupes = ''yes'''+char(13)
+'from '+char(13)
+'vic_orderdetails a '+char(13)
+'join '+char(13)
+'vic_orderdetails b '+char(13)
+'on '+char(13)
+'a.orderid = b.orderid '+char(13)
+'where '+char(13)
+'a.vic_srn > b.vic_srn '+char(13)
exec(@sql)
if object_id(@tablename) is not null
begin
exec('select count(*) as ''Number of Duplicates'' from '+@tablename+' where dupes is not null')
end
Print 'The Number of Duplicates are '+convert(varchar(100),@no_duplicates)
end
else
Print 'Invalid Table and Column Name'
a.Checks for the valid column and tablename.
b. Creates an Srn (identity column).
c. Creates a column dupe
d.Flags Dupes wherever duplicate records found
The Code for the Stored Procedure is as follows
GO
/****** Object: StoredProcedure [dbo].[remove_duplicates] ******/
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
GO
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
GO
ALTER procedure [dbo].[remove_duplicates]
@colname varchar(200)
,@tablename varchar(100)
as
set nocount on
declare @sql varchar(1000)
declare @no_duplicates int
--Check for the Table and Column Name
set @sql=''
if exists
(
select * from syscolumns where name like +''+@colname+'' and id = object_id(+''+@tablename+'')
)
begin
--Generate an SRN Number
if exists(select * from syscolumns where id = object_id(+''+@tablename+'') and name like 'Vic_srn')
begin
set @sql=''
set @sql = @sql + 'alter table '+@tablename+ ' drop column Vic_srn'
exec(@sql)
end
set @sql=''
set @sql = @sql+'alter table '+@tablename+ ' add Vic_srn numeric(6) identity(1,1)'
exec(@sql)
--Add a column for Dupes
if exists(select * from syscolumns where id = object_id(+''+@tablename+'') and name like 'dupes')
begin
set @sql=''
set @sql = @sql + 'alter table '+@tablename+ ' drop column dupes'
exec(@sql)
end
set @sql=''
set @sql=@sql+' alter table '+@tablename+ ' add dupes varchar(10)'
exec(@sql)
--Update the Column Dupes
set @sql=''
set @sql=@sql+'update a '+char(13)
+'set a.dupes = ''yes'''+char(13)
+'from '+char(13)
+'vic_orderdetails a '+char(13)
+'join '+char(13)
+'vic_orderdetails b '+char(13)
+'on '+char(13)
+'a.orderid = b.orderid '+char(13)
+'where '+char(13)
+'a.vic_srn > b.vic_srn '+char(13)
exec(@sql)
if object_id(@tablename) is not null
begin
exec('select count(*) as ''Number of Duplicates'' from '+@tablename+' where dupes is not null')
end
Print 'The Number of Duplicates are '+convert(varchar(100),@no_duplicates)
end
else
Print 'Invalid Table and Column Name'
Sunday, October 01, 2006
Simple TSQL - Calculating Age in TSQL
This is a stored procedure for calculating the age in Number of years and days
create procedure calculate_age
@birthday datetime
as
declare @yeardiff int
declare @daydiff int
declare @result varchar(100)
set @yeardiff = datediff(yy,@birthday,getdate())
if dateadd(yy,@yeardiff,@birthday) > getdate()
set @daydiff = datediff(dd,dateadd(yy,@yeardiff-1,@birthday),getdate())
else
set @daydiff = datediff(dd,dateadd(yy,@yeardiff,@birthday),getdate())
set @result = 'The age is '+convert(varchar,@yeardiff)+' years and '+ convert(varchar,@daydiff)+' days '
select @result
create procedure calculate_age
@birthday datetime
as
declare @yeardiff int
declare @daydiff int
declare @result varchar(100)
set @yeardiff = datediff(yy,@birthday,getdate())
if dateadd(yy,@yeardiff,@birthday) > getdate()
set @daydiff = datediff(dd,dateadd(yy,@yeardiff-1,@birthday),getdate())
else
set @daydiff = datediff(dd,dateadd(yy,@yeardiff,@birthday),getdate())
set @result = 'The age is '+convert(varchar,@yeardiff)+' years and '+ convert(varchar,@daydiff)+' days '
select @result
Sunday, September 03, 2006
System Tables : Part 1
/* Security Context of the Database */
--sql logins for the Database
---------------------------
select uid,status,name,convert(varchar(20),createdate) as Createddate,convert(varchar(20),updatedate) as Lastupdated from sysusers where isntname = 0
-- windows logins for Database
--------------------------------------
select uid,status,name,convert(varchar(20),createdate) as Createddate,convert(varchar(20),updatedate) as Lastupdated from sysusers where isntname = 1
--windows groups for the Database
--------------------------------
select uid,status,name,convert(varchar(20),createdate)as Createddate ,convert(varchar(20),updatedate) as Lastupdated from sysusers where isntgroup = 1
--Finding the Sql users not having logins
------------------------------------
select uid,status,name,convert(varchar(20),createdate) as Createddate,convert(varchar(20),updatedate) as Lastupdated from sysusers where issqluser = 1
--Find the useraccounts having dbaccess
----------------------------------------------------
select uid,status,name,convert(varchar(20),createdate) as Createddate,convert(varchar(20),updatedate) as Lastupdated from sysusers where hasdbaccess = 1
--Stored Procedures
--Displaying the Name and Text of the Stored Procedures.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
select so.id,so.name,sys.text from sysobjects sojoin syscomments sys on so.id = sys.idwhere so.xtype ='p'and so.base_schema_ver = 0
--Displaying the Stored Procedures which are Encrypted.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
select so.id,so.name from sysobjects sojoin syscomments sys on so.id = sys.idwhere so.xtype ='p'and so.base_schema_ver = 0and sys.encrypted = 1
--Displaying all the Columns for a particular Table in T-SQL
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
select sys.name from syscolumns sys join sysobjects soon sys.id = so.id where so.name ='Orders'
--Displaying the Columns in the Table having the Identity Columns
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
select name from syscolumns where status = 0x08
--sql logins for the Database
---------------------------
select uid,status,name,convert(varchar(20),createdate) as Createddate,convert(varchar(20),updatedate) as Lastupdated from sysusers where isntname = 0
-- windows logins for Database
--------------------------------------
select uid,status,name,convert(varchar(20),createdate) as Createddate,convert(varchar(20),updatedate) as Lastupdated from sysusers where isntname = 1
--windows groups for the Database
--------------------------------
select uid,status,name,convert(varchar(20),createdate)as Createddate ,convert(varchar(20),updatedate) as Lastupdated from sysusers where isntgroup = 1
--Finding the Sql users not having logins
------------------------------------
select uid,status,name,convert(varchar(20),createdate) as Createddate,convert(varchar(20),updatedate) as Lastupdated from sysusers where issqluser = 1
--Find the useraccounts having dbaccess
----------------------------------------------------
select uid,status,name,convert(varchar(20),createdate) as Createddate,convert(varchar(20),updatedate) as Lastupdated from sysusers where hasdbaccess = 1
--Stored Procedures
--Displaying the Name and Text of the Stored Procedures.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
select so.id,so.name,sys.text from sysobjects sojoin syscomments sys on so.id = sys.idwhere so.xtype ='p'and so.base_schema_ver = 0
--Displaying the Stored Procedures which are Encrypted.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
select so.id,so.name from sysobjects sojoin syscomments sys on so.id = sys.idwhere so.xtype ='p'and so.base_schema_ver = 0and sys.encrypted = 1
--Displaying all the Columns for a particular Table in T-SQL
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
select sys.name from syscolumns sys join sysobjects soon sys.id = so.id where so.name ='Orders'
--Displaying the Columns in the Table having the Identity Columns
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
select name from syscolumns where status = 0x08
General Sql Server Backup in my organisation
The Sql Server Backup Plan
a.Scheduling a FullDiskBackup of the Databases at 8:00 AM in the Morning (before the office starts)
b.Doing a Transactional log for every 3 hours for each database applications alternatively one hour
Eg : Database Application A - 9:00 AM ; 12:00AM ; 3:00 PM;6:30PM
Database Application B - 9:30 AM ; 12:30AM ; 3:30 PM ;6:30PM
As the Number of database applications increase we try to decrease the time slot between the 2 databasesThe entire Disk Backup is then Copied back to the Main Veritas Backup System(Regular Backup System)
We take the Daily Backup tapes with us and we store the weekly Backups in a Remote LocationWhen the Month Ending tapes are ready we store these tapes and get back the weekly backups for the Next weekly usage
a.Scheduling a FullDiskBackup of the Databases at 8:00 AM in the Morning (before the office starts)
b.Doing a Transactional log for every 3 hours for each database applications alternatively one hour
Eg : Database Application A - 9:00 AM ; 12:00AM ; 3:00 PM;6:30PM
Database Application B - 9:30 AM ; 12:30AM ; 3:30 PM ;6:30PM
As the Number of database applications increase we try to decrease the time slot between the 2 databasesThe entire Disk Backup is then Copied back to the Main Veritas Backup System(Regular Backup System)
We take the Daily Backup tapes with us and we store the weekly Backups in a Remote LocationWhen the Month Ending tapes are ready we store these tapes and get back the weekly backups for the Next weekly usage
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)